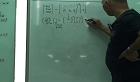The membrane-based dehumidification method is economical and environmentally friendly. Furthermore, the hollow fiber type membrane (HFM) has superior dehumidification performance because it has a large contact area. Despite many advantages, the membra...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.



Experimental and numerical analysis for predicting the dehumidification performance of a hollow fiber type membrane using the log mean pressure difference method
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A105941617
- 저자
- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2018
-
작성언어
English
- 주제어
-
등재정보
KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
자료형태
학술저널
-
수록면
5475-5481(7쪽)
-
KCI 피인용횟수
3
- 제공처
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
The membrane-based dehumidification method is economical and environmentally friendly. Furthermore, the hollow fiber type membrane (HFM) has superior dehumidification performance because it has a large contact area. Despite many advantages, the membranebased dehumidification method is still in the research and development stage, its use in the field is limited, and research on technology to integrate systems is insufficient. In this study, the relationships between parameters affecting dehumidification performance in terms of dehumidification rate and dehumidification amount were compared in order to apply the membrane-based dehumidification system in the field. The experimental and simulation values were compared in order to find a correlation with the dehumidification amount (or water fraction). Dehumidification performance increased when dry-bulb temperature, relative humidity, and log mean temperature difference (LMPD) were increased. The results of this study can be used to predict system performance in advance when a membrane-based dehumidification system is applied in the field.
참고문헌 (Reference)
1 A. Fick, "Ueber diffusion" 94 : 59-86, 1855
2 N. B. Houreh, "Three-dimensional CFD modeling of a planar membrane humidifier for PEM fuel cell systems" 39 (39): 14969-14979, 2014
3 L. Schoen, "Thermal environmental conditions for human occupancy, ANSI/ASHRAE Standard, 55-2013"
4 W.-P. Breugem, "The effective viscosity of a channel-type porous medium" 19 (19): 103104-103104-8, 2007
5 X. N. Wu, "Review on substrate of solid desiccant dehumidification system" 82 : 3236-3249, 2017
6 H.-X. Fu, "Review of the impact of liquid desiccant dehumidification on indoor air quality" 116 : 158-172, 2017
7 F. Manzano-Agugliaro, "Review of bioclimatic architecture strategies for achieving thermal comfort" 49 : 736-755, 2015
8 T. D. Bui, "On the theoretical and experimental energy efficiency analyses of a vacuum-based dehumidification membrane" 539 : 76-87, 2017
9 M. Musa, "Novel evaporative cooling systems for building applications" The University of Nottingham 2009
10 C. Pengilley, "Membranes for gas separation" University of Bath 2015
1 A. Fick, "Ueber diffusion" 94 : 59-86, 1855
2 N. B. Houreh, "Three-dimensional CFD modeling of a planar membrane humidifier for PEM fuel cell systems" 39 (39): 14969-14979, 2014
3 L. Schoen, "Thermal environmental conditions for human occupancy, ANSI/ASHRAE Standard, 55-2013"
4 W.-P. Breugem, "The effective viscosity of a channel-type porous medium" 19 (19): 103104-103104-8, 2007
5 X. N. Wu, "Review on substrate of solid desiccant dehumidification system" 82 : 3236-3249, 2017
6 H.-X. Fu, "Review of the impact of liquid desiccant dehumidification on indoor air quality" 116 : 158-172, 2017
7 F. Manzano-Agugliaro, "Review of bioclimatic architecture strategies for achieving thermal comfort" 49 : 736-755, 2015
8 T. D. Bui, "On the theoretical and experimental energy efficiency analyses of a vacuum-based dehumidification membrane" 539 : 76-87, 2017
9 M. Musa, "Novel evaporative cooling systems for building applications" The University of Nottingham 2009
10 C. Pengilley, "Membranes for gas separation" University of Bath 2015
11 M. Qu, "Isothermal membrane-based air dehumidification: A comprehensive review" 82 : 4060-4069, 2017
12 J.-G. Kim, "Indoor thermal environment of temporary mobile energy shelter houses (MeSHs) in South Korea" 8 (8): 11139-11152, 2015
13 X. Cheng, "Hybrid membranes for pervaporation separations" 541 : 329-346, 2017
14 T. D. Bui, "Experimental and modeling analysis of membrane-based air dehumidification" 144 : 114-122, 2015
15 E. Afshari, "Effects of the cell thermal behavior and water phase change on a proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance" 51 (51): 655-662, 2010
16 C. F. Wan, "Design and fabrication of hollow fiber membrane modules" 538 : 96-107, 2017
17 M. Sahlot, "Desiccant cooling systems: A review" 11 (11): 489-505, 2016
18 A. Seltzer, "Conceptual design of supercritical O2-based PC boiler final report" Foster Wheeler Power Group, Inc 2006
19 P. Cyklis, "Application of porous media flow model for the regenerator fluidised bed simulation" 9 : 229-236, 2017
20 M. Sultan, "An overview of solid desiccant dehumidification and air conditioning systems" 46 : 16-29, 2015
21 ANSYS, "ANSYS FLUENT user’s guide, release 18.1"
22 O. Amer, "A review of evaporative cooling technologies" 6 (6): 111-117, 2015
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
Magneto-rheological engine mount design and experimental characterization
- 대한기계학회
- Tamer Türkücü
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
Experimental study of biomass combustion and separation using vertical cyclone combustor
- 대한기계학회
- Ahmed Gharib
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
- 대한기계학회
- Harjeet S. Mann
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
- 대한기계학회
- Stasys Steišūnas
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
분석정보
인용정보 인용지수 설명보기
학술지 이력
| 연월일 | 이력구분 | 이력상세 | 등재구분 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 평가예정 | 해외DB학술지평가 신청대상 (해외등재 학술지 평가) | |
| 2020-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (해외등재 학술지 평가) |  |
| 2012-11-05 | 학술지명변경 | 한글명 : 대한기계학회 영문 논문집 -> Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology |  |
| 2010-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2008-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2006-01-19 | 학술지명변경 | 한글명 : KSME International Journal -> 대한기계학회 영문 논문집외국어명 : KSME International Journal -> Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology |  |
| 2006-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2004-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2001-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 선정 (등재후보2차) |  |
| 1998-07-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) |  |
학술지 인용정보
| 기준연도 | WOS-KCI 통합IF(2년) | KCIF(2년) | KCIF(3년) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 1.04 | 0.51 | 0.84 |
| KCIF(4년) | KCIF(5년) | 중심성지수(3년) | 즉시성지수 |
| 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.369 | 0.12 |




 ScienceON
ScienceON