Purpose: Hrd1 has recently emerged as a critical regulator of B-cells in autoimmune diseases. However, its role in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) remains largely unexplored. This study aimed to examine Hrd1 expre...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.



Differential Hrd1 Expression and B-Cell Accumulation in Eosinophilic and Non-eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A105981772
-
저자
Kun Chen (Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine) ; Miaomiao Han (Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine) ; Mengyao Tang (Tongji University School of Medicine) ; Yadong Xie (Chinese Academy of Sciences) ; Yuting Lai (Fudan University) ; Xianting Hu (Fudan University) ; Jia Zhang (Fudan University) ; Jun Yang (Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine) ; Huabin Li (Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine)

- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2018
-
작성언어
English
- 주제어
-
등재정보
KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
자료형태
학술저널
-
수록면
698-715(18쪽)
-
KCI 피인용횟수
0
- 제공처
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
Purpose: Hrd1 has recently emerged as a critical regulator of B-cells in autoimmune diseases. However, its role in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) remains largely unexplored. This study aimed to examine Hrd1 expression and B-cell accumulation and their possible roles in CRSwNP.
Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunohistochemistry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting were used to assess gene and protein expression in nasal tissue extracts. Cells isolated from nasal tissues and peripheral blood mononuclear cells were characterized by flow cytometry. Local antibody production was measured in tissue extracts with a Bio-Plex assay. Additionally, changes in Hrd1 expression in response to specific inflammatory stimuli were measured in cultured dispersed polyp cells.
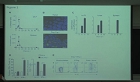
Results: Nasal polyps (NPs) from patients with eosinophilic CRSwNP (ECRS) had increased levels of Hrd1, B-cells and plasma cells compared with NPs from patients with non-eosinophilic CRSwNP (non-ECRS) or other control subjects (P < 0.05). The average Hrd1 levels in B-cells in NPs from ECRS patients were significantly higher than those from non-ECRS patients and control subjects (P < 0.05). NPs also contained significantly increased levels of several antibody isotypes compared with normal controls (P < 0.05). Interestingly, Hrd1 expression in cultured polyp cells from ECRS patients, but not non-ECRS patients, was significantly increased by interleukin-1β, lipopolysaccharide and Poly(I:C) stimulation, and inhibited by dexamethasone treatment (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Differential Hrd1 expression and B-cell accumulation between the ECRS and non-ECRS subsets suggests that they can exhibit distinct pathogenic mechanisms and play important roles in NP.
참고문헌 (Reference)
1 Jacobsen EA, "The expanding role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease" 120 : 3882-3890, 2012
2 Guerriero CJ, "The delicate balance between secreted protein folding and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation in human physiology" 92 : 537-576, 2012
3 Wei Y, "The antimicrobial protein short palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone 1 (SPLUNC1) is differentially modulated in eosinophilic and noneosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps" 133 : 420-428.e10, 2014
4 Xu Y, "The ER membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase Hrd1 is a positive regulator of T-cell immunity" 7 : 12073-, 2016
5 Amano T, "Synoviolin/Hrd1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, as a novel pathogenic factor for arthropathy" 17 : 2436-2449, 2003
6 Gao B, "Synoviolin promotes IRE1 ubiquitination and degradation in synovial fibroblasts from mice with collagen-induced arthritis" 9 : 480-485, 2008
7 Van Zele T, "Staphylococcus aureus colonization and IgE antibody formation to enterotoxins is increased in nasal polyposis" 114 : 981-983, 2004
8 Hsu J, "Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp" 25 : 285-290, 2011
9 Hulse KE, "Pathogenesis of nasal polyposis" 45 : 328-346, 2015
10 Toh ML, "Overexpression of synoviolin in peripheral blood and synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients and continued elevation in nonresponders to infliximab treatment" 54 : 2109-2118, 2006
1 Jacobsen EA, "The expanding role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease" 120 : 3882-3890, 2012
2 Guerriero CJ, "The delicate balance between secreted protein folding and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation in human physiology" 92 : 537-576, 2012
3 Wei Y, "The antimicrobial protein short palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone 1 (SPLUNC1) is differentially modulated in eosinophilic and noneosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps" 133 : 420-428.e10, 2014
4 Xu Y, "The ER membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase Hrd1 is a positive regulator of T-cell immunity" 7 : 12073-, 2016
5 Amano T, "Synoviolin/Hrd1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, as a novel pathogenic factor for arthropathy" 17 : 2436-2449, 2003
6 Gao B, "Synoviolin promotes IRE1 ubiquitination and degradation in synovial fibroblasts from mice with collagen-induced arthritis" 9 : 480-485, 2008
7 Van Zele T, "Staphylococcus aureus colonization and IgE antibody formation to enterotoxins is increased in nasal polyposis" 114 : 981-983, 2004
8 Hsu J, "Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp" 25 : 285-290, 2011
9 Hulse KE, "Pathogenesis of nasal polyposis" 45 : 328-346, 2015
10 Toh ML, "Overexpression of synoviolin in peripheral blood and synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients and continued elevation in nonresponders to infliximab treatment" 54 : 2109-2118, 2006
11 Zhang YN, "Nasal IL-4(+)CXCR5(+)CD4(+) T follicular helper cell counts correlate with local IgE production in eosinophilic nasal polyps" 137 : 462-473, 2016
12 Wen W, "Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy" 129 : 1522-1528.e5, 2012
13 Dilidaer, "Increased BAFF expression in nasal polyps is associated with local IgE production, Th2 response and concomitant asthma" 274 : 1883-1890, 2017
14 Schleimer RP, "Immunopathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis" 12 : 331-357, 2017
15 Hulse KE, "Immune mechanisms of chronic rhinosinusitis" 16 : 1-, 2016
16 Roza Khalmuratova, "Immune Cell Responses and Mucosal Barrier Disruptions in Chronic Rhinosinusitis" 대한면역학회 17 (17): 60-67, 2017
17 Yang H, "Hrd1-mediated BLIMP-1 ubiquitination promotes dendritic cell MHCII expression for CD4 T cell priming during inflammation" 211 : 2467-2479, 2014
18 Hamilos DL, "Host-microbial interactions in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis" 133 : 640-653.e4, 2014
19 Ishii KJ, "Host innate immune receptors and beyond: making sense of microbial infections" 3 : 352-363, 2008
20 Payne SC, "Genetics and phenotyping in chronic sinusitis" 128 : 710-720, 2011
21 Lindqvist M, "Expansion of HIV-specific T follicular helper cells in chronic HIV infection" 122 : 3271-3280, 2012
22 Kato A, "Evidence of a role for B cell-activating factor of the TNF family in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps" 121 : 1385-1392.e2, 2008
23 Tan BK, "Evidence for intranasal antinuclear autoantibodies in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps" 128 : 1198-1206.e1, 2011
24 Chu VT, "Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow" 12 : 151-159, 2011
25 Akdis CA, "Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: a PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology" 131 : 1479-1490, 2013
26 Kong S, "Endoplasmic reticulum-resident E3 ubiquitin ligase Hrd1 controls B-cell immunity through degradation of the death receptor CD95/Fas" 113 : 10394-10399, 2016
27 Lund FE, "Effector and regulatory B cells: modulators of CD4+ T cell immunity" 10 : 236-247, 2010
28 Song J, "Ectopic lymphoid tissues support local immunoglobulin production in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps" 141 : 927-937, 2018
29 Fokkens WJ, "EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists" 50 : 1-12, 2012
30 Luo Ba, "Distinct Inflammatory Profiles in Atopic and Nonatopic Patients With Chronic Rhinosinustis Accompanied by Nasal Polyps in Western China" 대한천식알레르기학회 7 (7): 346-358, 2015
31 Hulse KE, "Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is characterized by B-cell inflammation and EBV-induced protein 2 expression" 131 : 1075-1083.e7, 2013
32 Feldman S, "Chronic airway inflammation provides a unique environment for B cell activation and antibody production" 47 : 457-466, 2017
33 Kato A, "B-lymphocyte lineage cells and the respiratory system" 131 : 933-957, 2013
34 Dörner T, "B-cell-directed therapies for autoimmune disease" 5 : 433-441, 2009
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
- 대한천식알레르기학회
- Wat Mitthamsiri
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
KAAACI Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Cough in Adults and Children in Korea
- 대한천식알레르기학회
- 송대진
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
- 대한천식알레르기학회
- 김주희
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
- 대한천식알레르기학회
- YING LIU
- 2018
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
분석정보
인용정보 인용지수 설명보기
학술지 이력
| 연월일 | 이력구분 | 이력상세 | 등재구분 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 평가예정 | 해외DB학술지평가 신청대상 (해외등재 학술지 평가) | |
| 2020-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (해외등재 학술지 평가) |  |
| 2013-10-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 선정 (기타) |  |
| 2012-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 유지 (기타) |  |
| 2011-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보 1차 FAIL (등재후보1차) |  |
| 2010-07-14 | 학회명변경 | 한글명 : 대한알레르기학회 -> 대한천식알레르기학회영문명 : The Korean Academy Of Asthma And Allergy -> The Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology |  |
| 2009-01-01 | 평가 | SCOPUS 등재 (신규평가) |  |
학술지 인용정보
| 기준연도 | WOS-KCI 통합IF(2년) | KCIF(2년) | KCIF(3년) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2.43 | 0.8 | 1.86 |
| KCIF(4년) | KCIF(5년) | 중심성지수(3년) | 즉시성지수 |
| 1.55 | 1.38 | 0.89 | 0.15 |




 KCI
KCI