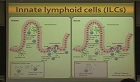
Intestinal fibrosis associated stricture is a common complication of inflammatory bowel disease usually requiring endoscopic or surgical intervention. Effective anti-fibrotic agents aiming to control or reverse intestinal fibrosis are still unavailabl...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.
https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A108586187
-
저자
Wu Xiaomin (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Lin Xiaoxuan (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Tan Jinyu (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Liu Zishan (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; He Jinshen (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Hu Fan (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Wang Yu (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Chen Minhu (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Liu Fen (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China) ; Mao Ren (Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China)

- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2023
-
작성언어
English
- 주제어
-
등재정보
KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
자료형태
학술저널
-
수록면
360-374(15쪽)
- DOI식별코드
- 제공처
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
Intestinal fibrosis associated stricture is a common complication of inflammatory bowel disease usually requiring endoscopic or surgical intervention. Effective anti-fibrotic agents aiming to control or reverse intestinal fibrosis are still unavailable. Thus, clarifying the mechanism underpinning intestinal fibrosis is imperative. Fibrosis is characterized by an excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins at the injured sites. Multiple cellular types are implicated in fibrosis development. Among these cells, mesenchymal cells are major compartments that are activated and then enhance the production of ECM. Additionally, immune cells contribute to the persistent activation of mesenchymal cells and perpetuation of inflammation. Molecules are messengers of crosstalk between these cellular compartments. Although inflammation is necessary for fibrosis development, purely controlling intestinal inflammation cannot halt the development of fibrosis, suggesting that chronic inflammation is not the unique contributor to fibrogenesis. Several inflammation-independent mechanisms including gut microbiota, creeping fat, ECM interaction, and metabolic reprogramming are involved in the pathogenesis of fibrosis. In the past decades, substantial progress has been made in elucidating the cellular and molecular mechanisms of intestinal fibrosis. Here, we summarized new discoveries and advances of cellular components and major molecular mediators that are associated with intestinal fibrosis, aiming to provide a basis for exploring effective anti-fibrotic therapies in this field.
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
- 거트앤리버 소화기연관학회협의회
- Kim Ju Young
- 2023
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
The Role of Endoscopic Management in Afferent Loop Syndrome
- 거트앤리버 소화기연관학회협의회
- Wu Clement Chun Ho
- 2023
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
- 거트앤리버 소화기연관학회협의회
- Shin Jaeseung
- 2023
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
National Survey Regarding the Management of Difficult Bile Duct Stones in South Korea
- 거트앤리버 소화기연관학회협의회
- Lee Yoon Suk
- 2023
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS







 KCI
KCI KISS
KISS