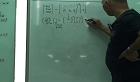In many estuaries and rivers, the contaminants such as heavy metals have became serious threat to ecosystem including human communities since eagerly development of heavy industrialization. It was found that such materials tended to bound with cohesiv...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.

탁도 측정을 통한 점착성 유사의 플록형성 분석 = Flocculation Analysis of Cohesive Sediment by Turbidity Measurement
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A106828005
- 저자
- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2020
-
작성언어
-
- 주제어
-
KDC
300
-
등재정보
KCI등재
-
자료형태
학술저널
-
수록면
49-55(7쪽)
- DOI식별코드
- 제공처
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
In many estuaries and rivers, the contaminants such as heavy metals have became serious threat to ecosystem including human communities since eagerly development of heavy industrialization. It was found that such materials tended to bound with cohesive sediments, and this bond mechanism is affected by hydraulic characteristics, for instance, turbulence intensity. To understand the complex relationship with the sediment-bond mechanism and hydrodynamics, the study for flocculation which includes the bond between sediment particles without heavy metals should be preceded as the first step. In this study, the flocculation of single sediment (Kaolin) was analysed through laboratory experiments in which the rotational jar-flow was generated and 3D numerical simulation which was performed to obtain the detailed flow fields and calculate hydraulic characteristics. First, the PIV experiment was conducted for the verification of 3D numerical model. And the flocculation index (IF) was proposed to consider the relation with the external energy and average turbulence length scale through the regression approach. The results showed that the flocculation was more affected by turbulence length (eddy size) than by turbulence intensity, and there was the significant specific range of turbulence length about formation of flocculation.
목차 (Table of Contents)
- 1. 서 론 2. 난류흐름에서의 플록형성 실험 3. 난류 흐름 수치모의 검증 4. 플록형성 지표(Flocculation Index) 5. 결 론
- 1. 서 론 2. 난류흐름에서의 플록형성 실험 3. 난류 흐름 수치모의 검증 4. 플록형성 지표(Flocculation Index) 5. 결 론
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
축대칭 함몰지형 위를 통과하는 파에 대한 확장형 완경사 방정식의 해석해
- 한국연안방재학회
- 정태화(Taehwa Jung)
- 2020
- KCI등재
-
공간분석을 활용한 해상교통관점의 해상풍력발전 최적지 영향요인 분석
- 한국연안방재학회
- 이정석(Jeong-Seok Lee)
- 2020
- KCI등재
-
이어도 종합해양과학기지의 진동 계측자료를 이용한 구조물 동특성 분석
- 한국연안방재학회
- 이진학(Jin-Hak Yi)
- 2020
- KCI등재
-
항공 및 드론 영상을 이용한 테트라포드 연안활동장소에 대한 공극률 계산 기법에 관한 연구
- 한국연안방재학회
- 전호군(Ho-Kun Jeon)
- 2020
- KCI등재




 스콜라
스콜라