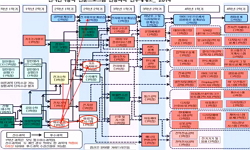
Urban problems are constantly occurring around the world due to rapid industrialization and population decline. In particular, as the number of vacant houses is gradually increasing as the population decreases, it is necessary to prepare countermeasur...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.

연결성 모델링을 활용한 빈집 녹지화 우선순위 평가 = Evaluation of Priorities for Greening of Vacant Houses using Connectivity Modeling
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A108049628
- 저자
- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2022
-
작성언어
Korean
- 주제어
-
등재정보
KCI등재
-
자료형태
학술저널
- 발행기관 URL
-
수록면
25-38(14쪽)
-
KCI 피인용횟수
0
- DOI식별코드
- 제공처
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
Urban problems are constantly occurring around the world due to rapid industrialization and population decline. In particular, as the number of vacant houses is gradually increasing as the population decreases, it is necessary to prepare countermeasures. A plan to utilize vacant houses has emerged to restore the natural environment of the urban ecosystem where forest destruction, damage to habitats of wild animals and plants, and disconnection have occurred due to large-scale development. Through connectivity analysis, it is possible to understand the overall ecosystem flow based on the movement of species and predict the effect when vacant houses are converted into green spaces. Therefore, this study analyzed the green area network to confirm the possibility of greening of vacant houses neglected in Jeonju based on circuit theory. Using Circuitscape and Least-cost path, we tried to identify the connectivity of green areas and propose an ecological axis based on the analysis. In order to apply the resistance values required for analysis based on previous studies, the 2020 subdivision land cover data were integrated into the major classification evaluation items. When the eight forests in the target site were analyzed as the standard, the overall connectivity and connectivity between forests in the area were high, so it is judged that the existing green areas can perform various functions, such as species movement and provision of habitats. Based on the results of the connectivity analysis, the importance of vacant houses was calculated and the top 20 vacant houses were identified, and it was confirmed that the higher the ranking, the more positive the degree of landscape connectivity was when converted to green areas. In addition, it was confirmed that the results of analyzing the least-cost path based on the resistance values such as connectivity analysis and the existing conceptual map showed some differences when comparing the ecological axes in the form. As a result of checking the vacant houses corresponding to the relevant axis based on the width standards of the main and sub-green areas, a total of 30 vacant houses were included in the 200m width and 6 vacant houses in the 80m width. It is judged that the conversion of vacant houses to green space can contribute to biodiversity conservation as well as connectivity between habitats of species as it is coupled with improved green space connectivity. In addition, it is expected to help solve the problem of vacant houses in the future by showing the possibility of using vacant houses.
참고문헌 (Reference)
1 박진경 ; 권혁삼, "커뮤니티 재생을 위한 빈집밀집구역의 실태조사와 재생방안 연구" 한국도시설계학회 20 (20): 5-18, 2019
2 허한결 ; 이동근 ; 모용원, "접근성과 생물다양성 증진을 고려한 도시 공원·녹지의 필요지역 선정 - 성남시를 사례로 -" 한국환경복원기술학회 18 (18): 13-26, 2015
3 박의준 ; 임미화, "전주시 빈집 핫스팟 지역 특성 분석" 한국주택학회 28 (28): 131-150, 2020
4 이동훈, "일본의 빈집문제 대응체계에 관한 고찰" 한국도시설계학회 18 (18): 51-61, 2017
5 홍석환 ; 최송현 ; 배정희 ; 이수동, "야생조류 이동통로 예측을 통한 도시녹지네트워크 설정연구" 한국지리정보학회 12 (12): 99-110, 2009
6 강완모 ; 박찬열, "수도권 지역 산림성 조류 서식지의 통로와 연결망 분석" 한국농림기상학회 17 (17): 191-201, 2015
7 채진확 ; 김정수 ; 구태회, "서울의 도시 비오톱에서 면적과 조류의 종수와의 관계" 한국환경생태학회 17 (17): 375-382, 2004
8 윤은주 ; 김은영 ; 김지연 ; 이동근, "생태축 제안을 위한 회로 이론 기초 연결성 평가" 한국환경영향평가학회 28 (28): 275-286, 2019
9 채우석, "빈집정비사업에 관한 법제적 연구" 법학연구소 (16) : 33-62, 2018
10 유재성 ; 이다예, "빈집의 물리적 실태와 위해성 수준에 따른 빈집 유형 분류" 한국도시지리학회 20 (20): 1-13, 2017
1 박진경 ; 권혁삼, "커뮤니티 재생을 위한 빈집밀집구역의 실태조사와 재생방안 연구" 한국도시설계학회 20 (20): 5-18, 2019
2 허한결 ; 이동근 ; 모용원, "접근성과 생물다양성 증진을 고려한 도시 공원·녹지의 필요지역 선정 - 성남시를 사례로 -" 한국환경복원기술학회 18 (18): 13-26, 2015
3 박의준 ; 임미화, "전주시 빈집 핫스팟 지역 특성 분석" 한국주택학회 28 (28): 131-150, 2020
4 이동훈, "일본의 빈집문제 대응체계에 관한 고찰" 한국도시설계학회 18 (18): 51-61, 2017
5 홍석환 ; 최송현 ; 배정희 ; 이수동, "야생조류 이동통로 예측을 통한 도시녹지네트워크 설정연구" 한국지리정보학회 12 (12): 99-110, 2009
6 강완모 ; 박찬열, "수도권 지역 산림성 조류 서식지의 통로와 연결망 분석" 한국농림기상학회 17 (17): 191-201, 2015
7 채진확 ; 김정수 ; 구태회, "서울의 도시 비오톱에서 면적과 조류의 종수와의 관계" 한국환경생태학회 17 (17): 375-382, 2004
8 윤은주 ; 김은영 ; 김지연 ; 이동근, "생태축 제안을 위한 회로 이론 기초 연결성 평가" 한국환경영향평가학회 28 (28): 275-286, 2019
9 채우석, "빈집정비사업에 관한 법제적 연구" 법학연구소 (16) : 33-62, 2018
10 유재성 ; 이다예, "빈집의 물리적 실태와 위해성 수준에 따른 빈집 유형 분류" 한국도시지리학회 20 (20): 1-13, 2017
11 한수경, "빈집의 공간적 군집과 고착화에 관한 실증 연구: 전라북도 익산시를 대상으로" 국토연구원 97 : 17-39, 2018
12 정수영 ; 전희정, "빈집 증가의 공간적 자기상관성에 대한 탐색적 연구" 대한국토·도시계획학회 54 (54): 89-102, 2019
13 이희연 ; 이영성, "맞춤형 빈집 활용을 위한 의사결정지원시스템 구축에 관한 연구" 한국도시지리학회 20 (20): 29-43, 2017
14 한수경 ; 이희연, "맞춤형 빈집 활용을 위한 근린주거환경 분석에 관한 연구" 한국도시지리학회 20 (20): 15-27, 2017
15 정혜진 ; 조은아 ; 고현서 ; 장갑수, "도시녹지에서 박새의 번식특성에 관한 연구" 한국환경복원기술학회 15 (15): 155-163, 2012
16 배민기 ; 정환도 ; 손영모, "기후변화대응을 위한 도시내 녹지공간의 역할 - 대전광역시를 사례로 -" 한국환경정책학회 17 (17): 181-199, 2009
17 강완모 ; 송영근 ; 김호걸 ; 김남춘 ; 송원경, "국내 육상경관 연결성의 정량적 분석 및 시각화" 한국지적정보학회 21 (21): 198-207, 2019
18 손은정 ; 맹희영 ; 이희연, "공폐가 밀집지역의 시 ・공간 패턴과 근린 부동산 가격에 미치는 영향 - 부산광역시를 대상으로 -" 한국부동산원 1 (1): 71-90, 2015
19 이창효 ; 김기중, "공간효과를 고려한 지역 간 빈집 증감의 영향요인 차이" 대한국토·도시계획학회 56 (56): 142-156, 2021
20 Finnerty Jr, T. A., "Youngstown 2010 Citywide Plan" The City of Youngstown 2000
21 Lerman, S. B., "Using urban forest assessmenttools to model bird habitat potential" 122 : 29-40, 2014
22 McRae, B. H., "Using circuit theory to model connectivity in ecology, evolution, and conservation" 89 (89): 2712-2724, 2008
23 Spear, S. F., "Use of resistance surfaces for landscape genetic studies : considerations for parameterization and analysis" 19 (19): 3576-3591, 2010
24 Shimazaki, A., "Urban permeability for birds : An approach combining mobbing-call experiments and circuit theory" 19 : 167-175, 2016
25 Koo, H, "Urban Shrinkage in Korea: Current Status and Policy Implications" Korea Research Institute for Human Settlements 2016
26 Jasmani, Z., "The influence of small urban parks characteristics on bird diversity : A case study of Petaling Jaya, Malaysia" 20 (20): 227-243, 2017
27 Koen, E. L., "The effect of map boundary on estimates of landscape resistance to animal movement" 5 (5): e11785-, 2010
28 Byun, BS, "Strategies for conserving green spaces for a pleasant urban environment" Korea Environment Institute 2002
29 Seong, E, "Shrinking-smart Policies for Revitalizing Neighborhoods in Shrinking Cities" Architecture&Urban Research Institute 2018
30 García-Sánchez, M. P., "Sex-specific connectivity modelling for brown bear conservation in the Carpathian Mountains" 1-19, 2021
31 Thayn, J. B., "Refining Hernando de Soto's route using electric circuit theory and Circuitscape" 68 (68): 595-602, 2016
32 Matheson, A., "Planning for Decline in Canadian Cites : Lessons from Youngstown, Ohio and Leinefelde" McGill University 2009
33 Marrotte, R. R., "Multi-species genetic connectivity in a terrestrial habitat network" 5 (5): 1-11, 2017
34 Banzhaf, E., "Monitoring, mapping and modelling urban decline : A multi-scale approach for Leipzig, Germany" 6 (6): 101-, 2007
35 Cao, Y., "Linking wilderness mapping and connectivity modelling : A methodological framework for wildland network planning" 251 : 108679-, 2020
36 Balbi, M., "Least-cost path analysis for urban greenways planning : A test with moths and birds across two habitats and two cities" 58 (58): 632-643, 2021
37 Song, W, "Landscape factors affecting the distribution of the great tit in fragmented urban forests of Seoul, South Korea" 12 (12): 73-83, 2016
38 Kwon, OS, "Landscape Ecological Analysis of Green Network in Urban Area Using Circuit Theory and Least-Cost Path" 10 (10): 847-, 2021
39 Desrochers, A., "Integrating GIS and homing experiments to study avian movement costs" 26 (26): 47-58, 2011
40 Schilling, J., "Greening the rust belt : A green infrastructure model for right sizing America's shrinking cities" 74 (74): 451-466, 2008
41 Wanghe, K., "Gravity model toolbox : An automated and open-source ArcGIS tool to build and prioritize ecological corridors in urban landscapes" 22 : e01012-, 2020
42 Desrochers, A., "Gap Crossing Decisions by Forest Songbirds during the Post Fledging Period : Decisíones de Cruce de Claros por Aves Paserinas de Bosques Durante el Periodo Post-Juvenil" 11 (11): 1204-1210, 1997
43 Gillies, C. S., "Fine-scale movement decisions of tropical forest birds in a fragmented landscape" 21 (21): 944-954, 2011
44 Tremblay, M. A., "Factors affecting the permeability of transportation and riparian corridors to the movements of songbirds in an urban landscape" 46 (46): 1314-1322, 2009
45 Zhang, Z., "Enhancing landscape connectivity through multifunctional green infrastructure corridor modeling and design" 38 : 305-317, 2019
46 Bowman, J., "Effects of cost surface uncertainty on current density estimates from circuit theory" 8 : e9617-, 2020
47 Nor, A. N. M., "Ecological connectivity networks in rapidly expanding cities" 3 (3): e00325-, 2017
48 Mimet, A., "Contribution of private gardens to habitat availability, connectivity and conservation of the common pipistrelle in Paris" 193 : 103671-, 2020
49 Poor, E. E., "Comparing habitat suitability and connectivity modeling methods for conserving pronghorn migrations" 7 (7): e49390-, 2012
50 McRae, B. H., "Circuitscape User’s Guide. ONLINE"
51 Dickson, B. G., "Circuit-theory applications to connectivity science and conservation" 33 (33): 239-249, 2019
52 St-Louis, V., "Circuit theory emphasizes the importance of edge-crossing decisions in dispersal-scale movements of a forest passerine" 29 (29): 831-841, 2014
53 Pelletier, D., "Applying circuit theory for corridor expansion and management at regional scales : tiling, pinch points, and omnidirectional connectivity" 9 (9): e84135-, 2014
54 Lim, HJ, "A plan to promote a super-block integrated and linked street housing maintenance project for the regeneration of multi-family and multi-family residential areas" The Seoul Institute 2020
55 Grafius, D. R., "A bird’s eye view : using circuit theory to study urban landscape connectivity for birds" 32 (32): 1771-1787, 2017
56 Jeonju City, "2035 Jeonju City Master Plan)" Jeonju City 2020
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
북한산림복구용 종자 변온침지 처리를 통한 발아특성 연구
- 한국환경복원기술학회
- 최종오
- 2022
- KCI등재
-
Post-2020 국가 보호지역 시스템 관리를 위한 기타 효과적인 지역 기반 보전 수단(OECMs) 후보지역 유형 검토
- 한국환경복원기술학회
- 심윤진
- 2022
- KCI등재
-
수도권 환경계획을 위한 초미세먼지 농도의 공간 군집특성과 고농도지역 분석
- 한국환경복원기술학회
- 임철희
- 2022
- KCI등재
-
잠정종자이동구역과 종분포모형을 이용한 자생 종자 분포 범위 연구
- 한국환경복원기술학회
- 김채영
- 2022
- KCI등재
분석정보
인용정보 인용지수 설명보기
학술지 이력
| 연월일 | 이력구분 | 이력상세 | 등재구분 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 평가예정 | 재인증평가 신청대상 (재인증) | |
| 2020-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (재인증) |  |
| 2017-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (계속평가) |  |
| 2013-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2010-06-09 | 학회명변경 | 한글명 : 한국환경복원녹화기술학회 -> 한국환경복원기술학회영문명 : The Korea Society For Environmental Restoration And Revegetation Technology -> The Korea Society of Environmental Restoration Technology |  |
| 2010-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2008-03-21 | 학술지명변경 | 한글명 : 한국환경복원녹화기술학회지 -> 한국환경복원기술학회지외국어명 : Journal of the Korea Society for Environmental Restoration and Revegetation Technology -> Journal of the Korea Society of Environmental Restoration Technology |  |
| 2008-01-01 | 평가 | 등재 1차 FAIL (등재유지) |  |
| 2006-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2003-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 선정 (등재후보2차) |  |
| 2002-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보 1차 PASS (등재후보1차) |  |
| 2001-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) |  |
학술지 인용정보
| 기준연도 | WOS-KCI 통합IF(2년) | KCIF(2년) | KCIF(3년) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.39 |
| KCIF(4년) | KCIF(5년) | 중심성지수(3년) | 즉시성지수 |
| 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.458 | 0.23 |




 ScienceON
ScienceON KISS
KISS