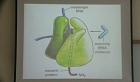
세포주기의 활성화, 그중에서도 측히 G1/S이행에 관여하는 세포주기조절 단백질들은 암발생에 있어서 매우 중요한 역할을 한다. p16단백질은 cyclin-dependent kinase 4 및 6와 결합하여 cyclin D1ㅇ 의...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.
폐암의 유전자 치료를 위한 Asenovirus-p16 vector의 제작에 관한 연구 = Inhibitory effect of adenovirus-mediated p16 gene transfer on the proliferation of lung cancer cell line
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=E685585
- 저자
- 발행기관
-
발행연도
1998년
-
작성언어
Korean
- 주제어
-
KDC
510.000
-
자료형태
한국연구재단(NRF)
-
수록면
1-29
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
국문 초록 (Abstract)
p16단백질은 cyclin-dependent kinase 4 및 6와 결합하여 cyclin D1ㅇ 의한 pRB단백질의 인산화를 억제하여 세포가 G1주기에서 S주기로 이행하는 것을 차단하는바, p16유전자의 변이는 많은 폐암 세포주 및 폐암조직에서 발견된다.
이렇게 자체로는 p16유전자가 결여된 폐암세포주에 wild-type의 p16유전자를 이입하면 세포의 증식과 세포주기의 진행을 억제함으로써 세포성장정지를 가져올 수 있을 것이라고 알려져 있다.
p16유전자의 종양억제기능을 알아보고, 이것이 암의 유전자치료에 적합한 유전자인지를 조사하기 위하여 p16유전자를 가진 재조합 아데노바이러스(ad-p16)를 제작하고 이를 이용하여 wild-type의 p16유전자를 이 단백질을 발현하지 못하는 비소세포폐암 세포주(NCI-H441, NCI-H157)에 이입하였다.
노던 블롯팅과 웨스턴 블롯팅을 통해서 ad-p16의 이입후 wild-type의 p16 전령 RNA 및 단백질이 가 세포주에서 발현되는 것을 확인할 수 있었으며, 면역세포화합법 결과 발현되 p16단백질은 세포의 핵에서 주로 발현되었다.
또한 ad-p16의 이입후 pRB단백질의 인산화가 억제되어 이 바이러스에 의해 생산되는 p16단백질의 기능을 확인할 수 있었다.
p16유전자가 결여된 비소세포폐암 세포주(NCI-H441, A549)의 성장은 ad-p16의 이입에 따른 wild-type의 p16단백질의 발현에 의해 억제되었으며, 연성한천 클론 정량법을 이용하여 관찰한 종양형성능도 발현된 p16단백질에 의해 유의하게 억제되었다.
Flow cytometry를 이용한 분석에 따르면 이러한 결과들은 세포주기중 G1주기에서의 차단과 관계 있었다.
이상의 결과들은 아데노바이러스를 이용한 p16INK4a유전자의 이입치료가 비소세포폐암의 유전자치료에 이용될 수 있을 가능성을 확인한 기초자료가 된다고 생각된다.
세포주기의 활성화, 그중에서도 측히 G1/S이행에 관여하는 세포주기조절 단백질들은 암발생에 있어서 매우 중요한 역할을 한다.
p16단백질은 cyclin-dependent kinase 4 및 6와 결합하여 cyclin D1ㅇ 의한 pRB단백질의 인산화를 억제하여 세포가 G1주기에서 S주기로 이행하는 것을 차단하는바, p16유전자의 변이는 많은 폐암 세포주 및 폐암조직에서 발견된다.
이렇게 자체로는 p16유전자가 결여된 폐암세포주에 wild-type의 p16유전자를 이입하면 세포의 증식과 세포주기의 진행을 억제함으로써 세포성장정지를 가져올 수 있을 것이라고 알려져 있다.
p16유전자의 종양억제기능을 알아보고, 이것이 암의 유전자치료에 적합한 유전자인지를 조사하기 위하여 p16유전자를 가진 재조합 아데노바이러스(ad-p16)를 제작하고 이를 이용하여 wild-type의 p16유전자를 이 단백질을 발현하지 못하는 비소세포폐암 세포주(NCI-H441, NCI-H157)에 이입하였다.
노던 블롯팅과 웨스턴 블롯팅을 통해서 ad-p16의 이입후 wild-type의 p16 전령 RNA 및 단백질이 가 세포주에서 발현되는 것을 확인할 수 있었으며, 면역세포화합법 결과 발현되 p16단백질은 세포의 핵에서 주로 발현되었다.
또한 ad-p16의 이입후 pRB단백질의 인산화가 억제되어 이 바이러스에 의해 생산되는 p16단백질의 기능을 확인할 수 있었다.
p16유전자가 결여된 비소세포폐암 세포주(NCI-H441, A549)의 성장은 ad-p16의 이입에 따른 wild-type의 p16단백질의 발현에 의해 억제되었으며, 연성한천 클론 정량법을 이용하여 관찰한 종양형성능도 발현된 p16단백질에 의해 유의하게 억제되었다.
Flow cytometry를 이용한 분석에 따르면 이러한 결과들은 세포주기중 G1주기에서의 차단과 관계 있었다.
이상의 결과들은 아데노바이러스를 이용한 p16INK4a유전자의 이입치료가 비소세포폐암의 유전자치료에 이용될 수 있을 가능성을 확인한 기초자료가 된다고 생각된다.
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
p16 gene inhibit cyclin D1 mediated pRB phosphorylation by combining with CDK4 and 6, and so block the G1/S transition of the cell, and abnormalities in p16 gene are found in many lung cancer cell line and primary lung cancer tissue. Replacement of wild-type p16 to these cancer cells which lack expression of endogenous p16 activity would suppress cell proliferation, and induce cell growth arrest by inhibiting cell cycle progression.
To examine its tumor suppressor function and its potential as an adequate gene in cancer gene therapy, recombinant adenovirus(ad-p16) which contain wild-type p16INK4a gene was produced and transfered into non-SCLS cell lines(NCI-H44I, NCI-H157) that do not express endogenous p16 protein.
Expression of wild-type p16 mRNA and protein in each cell lines after ad-p16 tranfer was showen by Northern and Western blot assay, and the expressed p16 protein was predominantly located in the nucleus of cell according to immuocytochemistry. The biologocal function of exogenous p16 protein was confirmed by the inhibition of phosphorylation of pRb protein.
Expression of exogenous p16 protein in non-SCLC cell lines(NCI-H441, A549) induced significant inhibition of cancer cell growth and colony formation in vitro, and these results were correlated with G1 cell cycle arrest according to flow cytometric analysis.
These results would be the basic research data which certified the value of adenovirally mediated p16INK4a gene therapy for non-SCLC.
Cell cycle regulatory proteins, especially involved in the G1/S transition of the cell cycle progression, play an important role in the development of cancer. p16 gene inhibit cyclin D1 mediated pRB phosphorylation by combining with CDK4 and 6, and s...
Cell cycle regulatory proteins, especially involved in the G1/S transition of the cell cycle progression, play an important role in the development of cancer.
p16 gene inhibit cyclin D1 mediated pRB phosphorylation by combining with CDK4 and 6, and so block the G1/S transition of the cell, and abnormalities in p16 gene are found in many lung cancer cell line and primary lung cancer tissue. Replacement of wild-type p16 to these cancer cells which lack expression of endogenous p16 activity would suppress cell proliferation, and induce cell growth arrest by inhibiting cell cycle progression.
To examine its tumor suppressor function and its potential as an adequate gene in cancer gene therapy, recombinant adenovirus(ad-p16) which contain wild-type p16INK4a gene was produced and transfered into non-SCLS cell lines(NCI-H44I, NCI-H157) that do not express endogenous p16 protein.
Expression of wild-type p16 mRNA and protein in each cell lines after ad-p16 tranfer was showen by Northern and Western blot assay, and the expressed p16 protein was predominantly located in the nucleus of cell according to immuocytochemistry. The biologocal function of exogenous p16 protein was confirmed by the inhibition of phosphorylation of pRb protein.
Expression of exogenous p16 protein in non-SCLC cell lines(NCI-H441, A549) induced significant inhibition of cancer cell growth and colony formation in vitro, and these results were correlated with G1 cell cycle arrest according to flow cytometric analysis.
These results would be the basic research data which certified the value of adenovirally mediated p16INK4a gene therapy for non-SCLC.
목차 (Table of Contents)
- 요약문
- 1. 서론
- 2. 연구재료 및 방법
- 요약문
- 1. 서론
- 2. 연구재료 및 방법
- 3. 결과
- 4. 논의
- 5. 결론
- 6. 참고문헌
- 7. 발표논문 및 초록첨부
- 8. 연구비 사용내역