Objective: To optimize the MR imaging protocol for coronary arterial wall depiction in vitro and characterize the coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Materials and Methods: MRI examination was prospectively performed in ten porcine hearts in order to o...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.



Optimizing the Imaging Protocol for Ex Vivo Coronary Artery Wall Using High-Resolution MRI: An Experimental Study on Porcine and Human
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A104532566
-
저자
Jiong Yang (The General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces) ; Tao Li (The General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces) ; Xiaoming Cui (The General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces) ; Weihua Zhou (The General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces) ; Xin Li (The General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces) ; Xinwu Zhang (The General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces)
- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2013
-
작성언어
English
- 주제어
-
등재정보
KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
자료형태
학술저널
-
수록면
581-588(8쪽)
-
KCI 피인용횟수
1
- DOI식별코드
- 제공처
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
Objective: To optimize the MR imaging protocol for coronary arterial wall depiction in vitro and characterize the coronary atherosclerotic plaques.
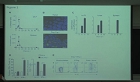
Materials and Methods: MRI examination was prospectively performed in ten porcine hearts in order to optimize the MR imaging protocol. Various surface coils were used for coronary arterial wall imaging with the same parameters. Then, the image parameters were further optimized for high-resolution coronary wall imaging. The signal-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-noise ratio (CNR) of images were measured. Finally, 8 human cadaver hearts with coronary atherosclerotic plaques were prospectively performed with MRI examination using optimized protocol in order to characterize the coronary atherosclerotic plaques.
Results: The SNR and CNR of MR image with temporomandibular coil were the highest of various surface coils. High-resolution and high SNR and CNR for ex vivo coronary artery wall depiction can be achieved using temporomandibular coil with 512 x 512 in matrix. Compared with histopathology, the sensitivity and specificity of MRI for identifying advanced plaques were: type IV-V (lipid, necrosis, fibrosis), 94% and 95%; type VI (hemorrhage), 100% and 98%; type VII (calcification), 91% and 100%; and type VIII (fibrosis without lipid core), 100% and 98%, respectively.
Conclusion: Temporomandibular coil appears to be dramatically superior to eight-channel head coil and knee coil for ex vivo coronary artery wall imaging, providing higher spatial resolution and improved the SNR. Ex vivo high-resolution MRI has capability to distinguish human coronary atherosclerotic plaque compositions and accurately classify advanced plaques.
참고문헌 (Reference)
1 Cury RC, "Vulnerable plaque detection by 3.0 tesla magnetic resonance imaging" 41 : 112-115, 2006
2 Fuster V, "The pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and the acute coronary syndromes (2)" 326 : 310-318, 1992
3 Fuster V, "The pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and the acute coronary syndromes (1)" 326 : 242-250, 1992
4 Kim WY, "Subclinical coronary and aortic atherosclerosis detected by magnetic resonance imaging in type 1 diabetes with and without diabetic nephropathy" 115 : 228-235, 2007
5 Stary HC, "Richardson M, et al. A definition of the intima of human arteries and of its atherosclerosis-prone regions. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association" 85 : 391-405, 1992
6 Virmani R, "Pathology of the vulnerable plaque" 47 (47): C13-C18, 2006
7 Nikolaou K, "Optimization of ex vivo CT- and MR- imaging of atherosclerotic vessel wall changes" 20 : 327-334, 2004
8 Nikolaou K, "Multidetector-row computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerotic lesions in human ex vivo coronary arteries" 174 : 243-252, 2004
9 Koops A, "Multicontrast-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerotic plaques at 3.0 and 1.5 Tesla: ex-vivo comparison with histopathologic correlation" 17 : 279-286, 2007
10 Macedo R, "MRI detects increased coronary wall thickness in asymptomatic individuals: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA)" 28 : 1108-1115, 2008
1 Cury RC, "Vulnerable plaque detection by 3.0 tesla magnetic resonance imaging" 41 : 112-115, 2006
2 Fuster V, "The pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and the acute coronary syndromes (2)" 326 : 310-318, 1992
3 Fuster V, "The pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and the acute coronary syndromes (1)" 326 : 242-250, 1992
4 Kim WY, "Subclinical coronary and aortic atherosclerosis detected by magnetic resonance imaging in type 1 diabetes with and without diabetic nephropathy" 115 : 228-235, 2007
5 Stary HC, "Richardson M, et al. A definition of the intima of human arteries and of its atherosclerosis-prone regions. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association" 85 : 391-405, 1992
6 Virmani R, "Pathology of the vulnerable plaque" 47 (47): C13-C18, 2006
7 Nikolaou K, "Optimization of ex vivo CT- and MR- imaging of atherosclerotic vessel wall changes" 20 : 327-334, 2004
8 Nikolaou K, "Multidetector-row computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerotic lesions in human ex vivo coronary arteries" 174 : 243-252, 2004
9 Koops A, "Multicontrast-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerotic plaques at 3.0 and 1.5 Tesla: ex-vivo comparison with histopathologic correlation" 17 : 279-286, 2007
10 Macedo R, "MRI detects increased coronary wall thickness in asymptomatic individuals: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA)" 28 : 1108-1115, 2008
11 Virmani R, "Lessons from sudden coronary death: a comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions" 20 : 1262-1275, 2000
12 Fayad ZA, "In vivo magnetic resonance evaluation of atherosclerotic plaques in the human thoracic aorta: a comparison with transesophageal echocardiography" 101 : 2503-2509, 2000
13 Yuan C, "In vivo accuracy of multispectral magnetic resonance imaging for identifying lipid-rich necrotic cores and intraplaque hemorrhage in advanced human carotid plaques" 104 : 2051-2056, 2001
14 Yuan C, "High-Resolution magnetic resonance imaging of normal and atherosclerotic human coronary arteries ex vivo: discrimination of plaque tissue components" 49 : 491-499, 2001
15 Gerretsen S, "Detection of coronary plaques using MR coronary vessel wall imaging: validation of findings with intravascular ultrasound" 23 : 115-124, 2013
16 Falk E, "Coronary plaque disruption" 92 : 657-671, 1995
17 Yuan C, "Contrast-enhanced high resolution MRI for atherosclerotic carotid artery tissue characterization" 15 : 62-67, 2002
18 Li T, "Classification of human coronary atherosclerotic plaques using ex vivo high-resolution multicontrast-weighted MRI compared with histopathology" 198 : 1069-1075, 2012
19 Cai JM, "Classification of human carotid atherosclerotic lesions with in vivo multicontrast magnetic resonance imaging" 106 : 1368-1373, 2002
20 Serfaty JM, "Atherosclerotic plaques: classification and characterization with T2-weighted high-spatial-resolution MR imaging-- an in vitro study" 219 : 403-410, 2001
21 Stary HC, "A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association" 89 : 2462-2478, 1994
22 Stary HC, "A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association" 92 : 1355-1374, 1995
23 권혜미, "3D Whole-Heart Coronary MR Angiography at 1.5T in Healthy Volunteers: Comparison between Unenhanced SSFP and Gd-Enhanced FLASH Sequences" 대한영상의학회 12 (12): 679-685, 2011
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
Hyperfunction Thyroid Nodules: Their Risk for Becoming or Being Associated with Thyroid Cancers
- 대한영상의학회
- 이은선
- 2013
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
- 대한영상의학회
- 송영규
- 2013
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
- 대한영상의학회
- Uei Pua
- 2013
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
-
Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Breast: MR Imaging Findings
- 대한영상의학회
- 임효순
- 2013
- KCI등재,SCIE,SCOPUS
분석정보
인용정보 인용지수 설명보기
학술지 이력
| 연월일 | 이력구분 | 이력상세 | 등재구분 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 평가예정 | 해외DB학술지평가 신청대상 (해외등재 학술지 평가) | |
| 2020-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (해외등재 학술지 평가) |  |
| 2016-11-15 | 학회명변경 | 영문명 : The Korean Radiological Society -> The Korean Society of Radiology |  |
| 2010-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2007-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 선정 (등재후보2차) |  |
| 2006-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보 1차 PASS (등재후보1차) |  |
| 2003-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) |  |
학술지 인용정보
| 기준연도 | WOS-KCI 통합IF(2년) | KCIF(2년) | KCIF(3년) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 1.61 | 0.46 | 1.15 |
| KCIF(4년) | KCIF(5년) | 중심성지수(3년) | 즉시성지수 |
| 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.494 | 0.06 |




 KCI
KCI